-

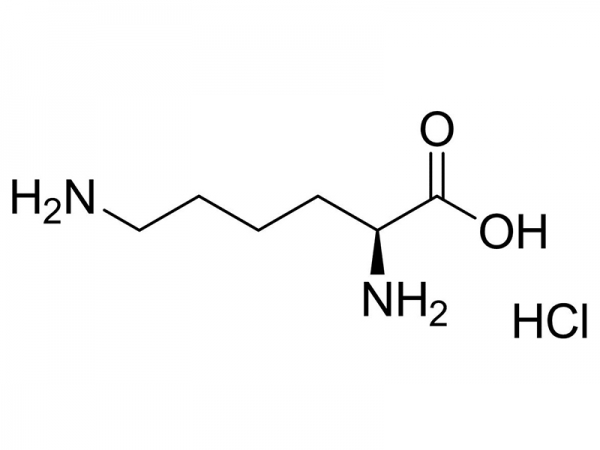
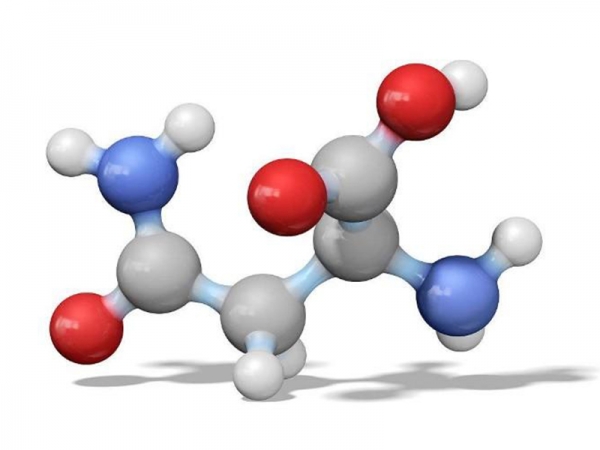
 Lysine is an essential amino acid, meaning that it is not able be synthesized in the body. It has the chemical formula HO2CCH(NH2)(CH2)4NH2, and its codons are AAA and AAG. L-lysine is the biologically active form of lysine in animalsL-lysine is the precursor for many substances that are important in human nutrition. Alpha ketoglutarate is used to convert L-lysine into acetyl-CoA, which plays an essential role in the citric acid cycle.
Lysine is an essential amino acid, meaning that it is not able be synthesized in the body. It has the chemical formula HO2CCH(NH2)(CH2)4NH2, and its codons are AAA and AAG. L-lysine is the biologically active form of lysine in animalsL-lysine is the precursor for many substances that are important in human nutrition. Alpha ketoglutarate is used to convert L-lysine into acetyl-CoA, which plays an essential role in the citric acid cycle. -

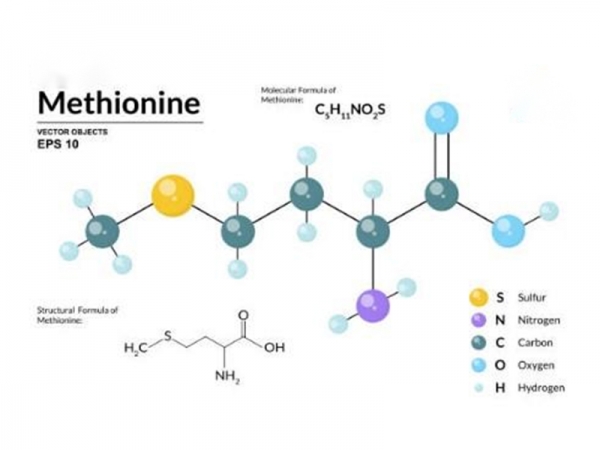
 L- Methionine, or methionine, is an essential amino acid found in the body used to make proteins and peptides. It’s found in meat, fish and dairy products, as well as nuts and grains. Think protein foods, and you will likely find methionine.
L- Methionine, or methionine, is an essential amino acid found in the body used to make proteins and peptides. It’s found in meat, fish and dairy products, as well as nuts and grains. Think protein foods, and you will likely find methionine. -

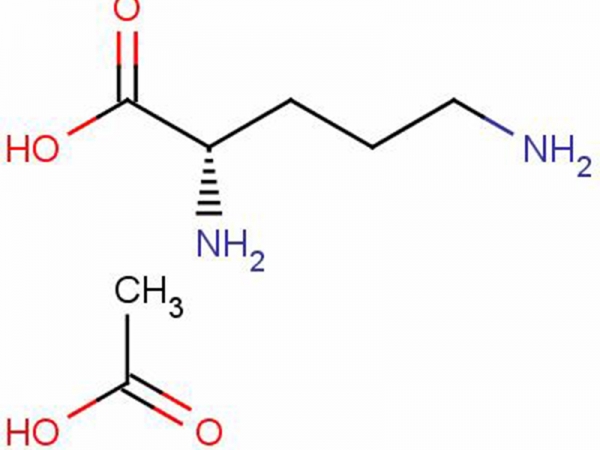
 L-Ornithine Alpha-Ketoglutarate (OKG) combines Alpha-Ketoglutaric Acid with Ornithine; the resulting compound increases protein availability and also speeds up the rate and effectiveness of the synthesis of amino acids.
L-Ornithine Alpha-Ketoglutarate (OKG) combines Alpha-Ketoglutaric Acid with Ornithine; the resulting compound increases protein availability and also speeds up the rate and effectiveness of the synthesis of amino acids. -

 Chlorhydrate d'Ornithine, L-Ornithine, L-Ornithine HCl ... Ornithine is a chemical called an amino acid. It is made in the body. It can also be made in a laboratory. People use it as a medicine. Ornithine is commonly used by mouth for improving athletic performance. It is also used for weight loss, wound healing, and to increase sleep quality.
Chlorhydrate d'Ornithine, L-Ornithine, L-Ornithine HCl ... Ornithine is a chemical called an amino acid. It is made in the body. It can also be made in a laboratory. People use it as a medicine. Ornithine is commonly used by mouth for improving athletic performance. It is also used for weight loss, wound healing, and to increase sleep quality. -

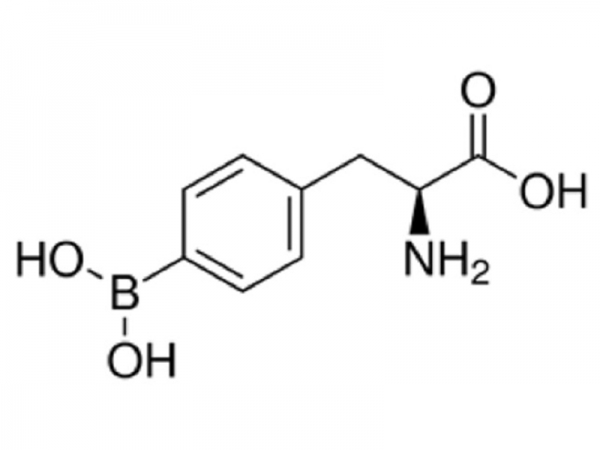
 L-Phenylalanine is an essential amino acid. It is the only form of phenylalanine found in proteins. Major dietary sources of L-phenylalanine include meat, fish, eggs, cheese, and milk.
L-Phenylalanine is an essential amino acid. It is the only form of phenylalanine found in proteins. Major dietary sources of L-phenylalanine include meat, fish, eggs, cheese, and milk. -

 L-Proline is one of the 20 amino acids that are used to synthesize proteins by the human body. L-proline is the only proteinogenic amino acid that is a secondary amine, meaning that its amine nitrogen is bound to two alkyl groups. Virtually all of the proteins in the human body contain L-proline, and the only amino acids that are more abundant are alanine and glutamine. L-proline is especially important in the production of collagen, which is a primary component in skin, cartilage and bone.
L-Proline is one of the 20 amino acids that are used to synthesize proteins by the human body. L-proline is the only proteinogenic amino acid that is a secondary amine, meaning that its amine nitrogen is bound to two alkyl groups. Virtually all of the proteins in the human body contain L-proline, and the only amino acids that are more abundant are alanine and glutamine. L-proline is especially important in the production of collagen, which is a primary component in skin, cartilage and bone. -

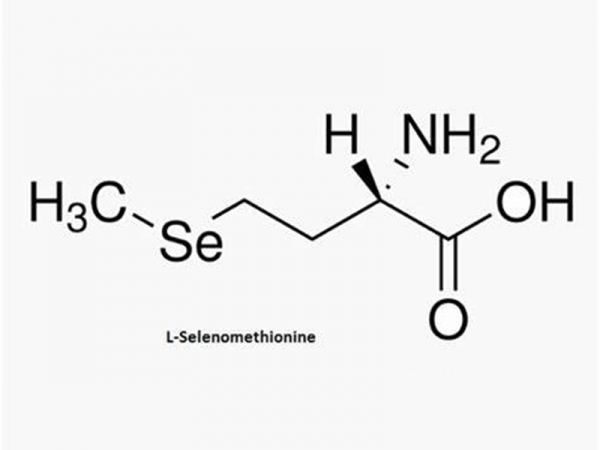
 L-Selenomethionine is the amino acid methionine with selenium substituting for the sulphur moiety. Methionine is an essential amino acid in humans, whereas selenium is a free-radical scavenging anti-oxidant, essential for the protection of various tissues from the damages of lipid peroxidation. As a trace mineral that is toxic in high doses, selenium is a cofactor for glutathione peroxidase.
L-Selenomethionine is the amino acid methionine with selenium substituting for the sulphur moiety. Methionine is an essential amino acid in humans, whereas selenium is a free-radical scavenging anti-oxidant, essential for the protection of various tissues from the damages of lipid peroxidation. As a trace mineral that is toxic in high doses, selenium is a cofactor for glutathione peroxidase. -

 Serine is an amino acid that plays a role in many biosynthetic pathways. It’s the major source of one-carbon units for methylation reactions that occur with the generation of S-adenosylmethionine.Serine, plays an important role in brain function and the health of the central nervous system. One of the many benefits of serine is its function in the formation of phospholipids that are needed for creating every single cell in the human body.
Serine is an amino acid that plays a role in many biosynthetic pathways. It’s the major source of one-carbon units for methylation reactions that occur with the generation of S-adenosylmethionine.Serine, plays an important role in brain function and the health of the central nervous system. One of the many benefits of serine is its function in the formation of phospholipids that are needed for creating every single cell in the human body. -

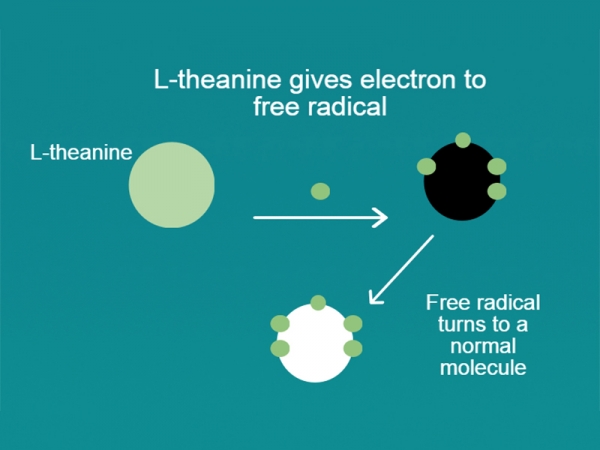
 L-Theanine (also called theanine, or sometimes r-glutamylethylamide) is an amino acid that impacts nerve impulses in the brain and the release of neurotransmitters, including GABA. It is known as natural ananxiolytic because it can have a calming, sedative effect on the body and mind without making you feel drowsy — which is why it’s often used to reduce anxiety, hyperactivity and sleep-related problems.
L-Theanine (also called theanine, or sometimes r-glutamylethylamide) is an amino acid that impacts nerve impulses in the brain and the release of neurotransmitters, including GABA. It is known as natural ananxiolytic because it can have a calming, sedative effect on the body and mind without making you feel drowsy — which is why it’s often used to reduce anxiety, hyperactivity and sleep-related problems. -

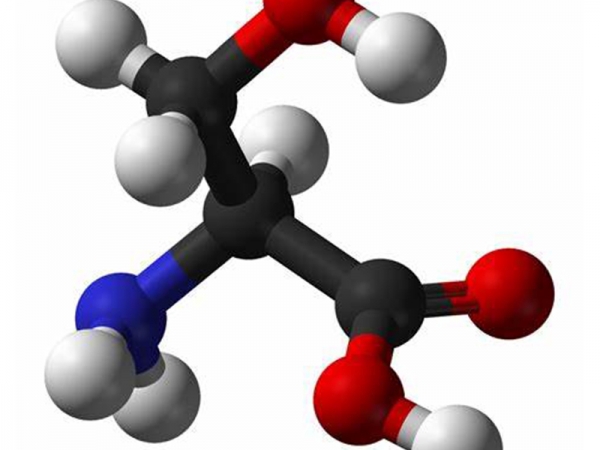
 Threonine is an essential amino acid that plays an important role in regulating protein balance in the body. Because it’s considered an “essential amino acid,” that means the body doesn’t synthesize the amino acid, so we need to eat foods high in threonine to obtain it.
Threonine is an essential amino acid that plays an important role in regulating protein balance in the body. Because it’s considered an “essential amino acid,” that means the body doesn’t synthesize the amino acid, so we need to eat foods high in threonine to obtain it. -

 Tryptophan (also called L-tryprophan) is an essential amino acid that acts like a natural mood regulator, since it has the ability to help the body produce and balance certain hormones naturally. Supplementing with tryptophan-rich foods or taking supplements helps bring on natural calming effects, induces sleep, fights anxiety and can also help burn more body fat. Tryptophan has also been found to stimulate the release of growth hormones and even reduce food cravings for carbohydrates and help kick a sugar addiction in some cases.
Tryptophan (also called L-tryprophan) is an essential amino acid that acts like a natural mood regulator, since it has the ability to help the body produce and balance certain hormones naturally. Supplementing with tryptophan-rich foods or taking supplements helps bring on natural calming effects, induces sleep, fights anxiety and can also help burn more body fat. Tryptophan has also been found to stimulate the release of growth hormones and even reduce food cravings for carbohydrates and help kick a sugar addiction in some cases. -

 Tyrosine, or L-tyrosine, is one of 20 amino acids that help build proteins. It is considered a “non-essential amino acid” because the body makes it from another amino acid called phenylalanine. This means you don’t need to get tyrosine from foods, although obtaining more from your diet can be helpful.
Tyrosine, or L-tyrosine, is one of 20 amino acids that help build proteins. It is considered a “non-essential amino acid” because the body makes it from another amino acid called phenylalanine. This means you don’t need to get tyrosine from foods, although obtaining more from your diet can be helpful.
Select your country