5-methyl-THF(5-Methyltetrahydrofolic acid) is the source of the one-carbon unit involved in the methylation of homocysteine to methionine by the enzyme tetrahydropteroylglutamate methyltransferase (5-methyltetrahydropteroyl-L-glutamate : L-homocysteine S-methyltransferase, EC 2.1.1.13), which has more commonly been called methionine synthetase. This enzyme requires methylcobalamin (vitamin B12) as coenzyme and the additional cofactors S-adenosylmethionine and reduced flavin. THF generated by this reaction is then added to the cell's THF pool and participates in a series of one-carbon transfers.
-


-


Acetyl L Carnitine, also usually abbreviated as ALCAR, is an acetylated form of L-carnitine, a supplement often used to support athletic performance. L-carnitine is a compound that is produced naturally in the body and transported to the heart, brain, and other tissues.
-


Lipoic acid (LA), also known as α-lipoic acid and alpha lipoic acid (ALA) and thioctic acid is an organosulfur compound derived from octanoic acid. ALA is made in animals normally, and is essential for aerobic metabolism. It is also manufactured and is available as a dietary supplement in some countries where it is marketed as an antioxidant, and is available as a pharmaceutical drug in other countries.
-


Astaxanthin is a keto-carotenoid. It belongs to a larger class of chemical compounds known as terpenes built from five carbon precursors, isopentenyl diphosphate, and dimethylallyl diphosphate. Astaxanthin is classified as a xanthophyll, but currently employed to describe carotenoid compounds that have oxygen-containing components, hydroxyl or ketone, such as zeaxanthin and canthaxanthin. Indeed, astaxanthin is a metabolite of zeaxanthin and/or canthaxanthin, containing both hydroxyl and ketone functional groups.
-


Beta-carotene is one of a group of red, orange, and yellow pigments called carotenoids. Beta-carotene and other carotenoids provide approximately 50% of the vitamin A needed in the American diet.There are many global health authorities that recommend getting beta-carotene and other antioxidants from food instead of supplements. Eating five servings of fruits and vegetables daily provides 6-8 mg of beta-carotene.
-


Chitosan is a linear polysaccharide composed of randomly distributed β-linked D-glucosamine and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine. It is made by treating the chitin shells of shrimp and other crustaceans with an alkaline substance, such as sodium hydroxide.
-


Choline is an essential nutrient for humans and many other animals. Choline occurs as a cation that forms various salts. Humans and most animals make choline de novo, but production is insufficient in humans and most species. Choline is often not classified as a vitamin, but as a nutrient with an amino acid–like metabolism.Choline is required to produce acetylcholine – a neurotransmitter – and S-adenosylmethionine, a universal methyl donor involved in the synthesis of homocysteine.
-


Chondroitin sulfate is a sulfated glycosaminoglycan composed of a chain of alternating sugars. It is usually found attached to proteins as part of a proteoglycan. A chondroitin chain can have over 100 individual sugars, each of which can be sulfated in variable positions and quantities. . Along with glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate has become a widely used dietary supplement for treatment of osteoarthritis.
-

 Citicoline, also known as cytidine diphosphate-choline or cytidine 5'-diphosphocholine is an intermediate in the generation of phosphatidylcholine from choline, a common biochemical process in cell membranes. Citicoline is naturally occurring in the cells of human and animal tissue, in particular the organs.
Citicoline, also known as cytidine diphosphate-choline or cytidine 5'-diphosphocholine is an intermediate in the generation of phosphatidylcholine from choline, a common biochemical process in cell membranes. Citicoline is naturally occurring in the cells of human and animal tissue, in particular the organs. -

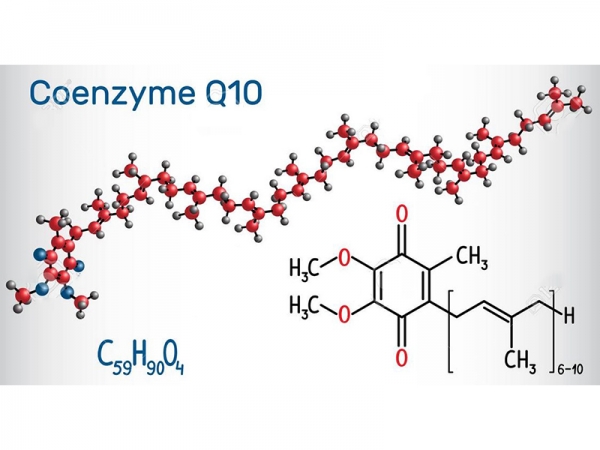
 Coenzyme Q, also known as ubiquinone, is a coenzyme family that is ubiquitous in animals and most bacteria. In humans, the most common form is Coenzyme Q₁₀ or ubiquinone-10. CoQ₁₀ is not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of any medical condition; however, it is sold as a dietary supplement and is an ingredient in some.
Coenzyme Q, also known as ubiquinone, is a coenzyme family that is ubiquitous in animals and most bacteria. In humans, the most common form is Coenzyme Q₁₀ or ubiquinone-10. CoQ₁₀ is not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of any medical condition; however, it is sold as a dietary supplement and is an ingredient in some. -

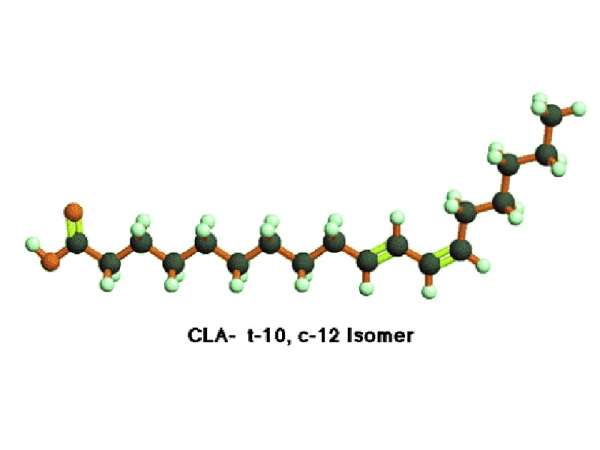
 Conjugated linoleic acid refers to a mixture of positional and geometric isomers of linoleic acid (18 carbons) with two double bonds separated by one single bond. Further, each double bond can be in the cis or trans configuration. Therefore, many forms of CLA are possible (Sehat et al., 1999; Yurawecz et al., 1999a, b), but the main form present in foods from ruminant animals is the cis- 9, trans-11 CLA, which was recently given the trivial name rumenic acid (RA; Kramer et al., 1998a). The presence of this fatty acid in ruminant products arises from its formation in the rumen. Conjugated linoleic acid is unique among the naturally occurring anticarcinogens in that it is potent at extremely low levels and present in foods from ruminant animals.
Conjugated linoleic acid refers to a mixture of positional and geometric isomers of linoleic acid (18 carbons) with two double bonds separated by one single bond. Further, each double bond can be in the cis or trans configuration. Therefore, many forms of CLA are possible (Sehat et al., 1999; Yurawecz et al., 1999a, b), but the main form present in foods from ruminant animals is the cis- 9, trans-11 CLA, which was recently given the trivial name rumenic acid (RA; Kramer et al., 1998a). The presence of this fatty acid in ruminant products arises from its formation in the rumen. Conjugated linoleic acid is unique among the naturally occurring anticarcinogens in that it is potent at extremely low levels and present in foods from ruminant animals. -

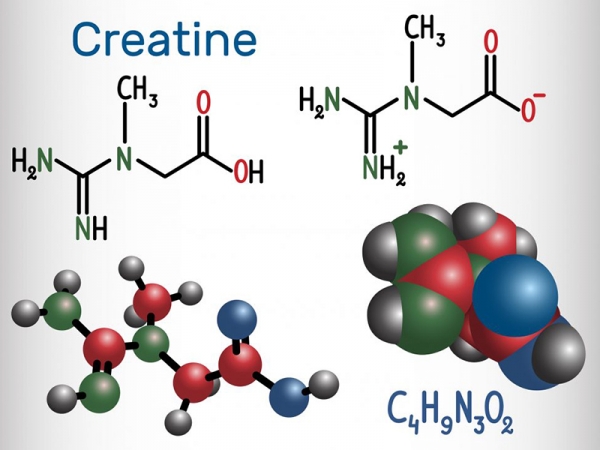
 Creatine is an organic compound with the nominal formula(HN)CN(CH₃)CH₂CO₂H. This species exists in various modifications in solution. Creatine is found in vertebrates where it facilitates recycling of adenosine triphosphate, the energy currency of the cell, primarily in muscle and brain tissue. Recycling is achieved by converting adenosine diphosphate back to ATP via donation of phosphate groups. Creatine also acts as a buffer.
Creatine is an organic compound with the nominal formula(HN)CN(CH₃)CH₂CO₂H. This species exists in various modifications in solution. Creatine is found in vertebrates where it facilitates recycling of adenosine triphosphate, the energy currency of the cell, primarily in muscle and brain tissue. Recycling is achieved by converting adenosine diphosphate back to ATP via donation of phosphate groups. Creatine also acts as a buffer.